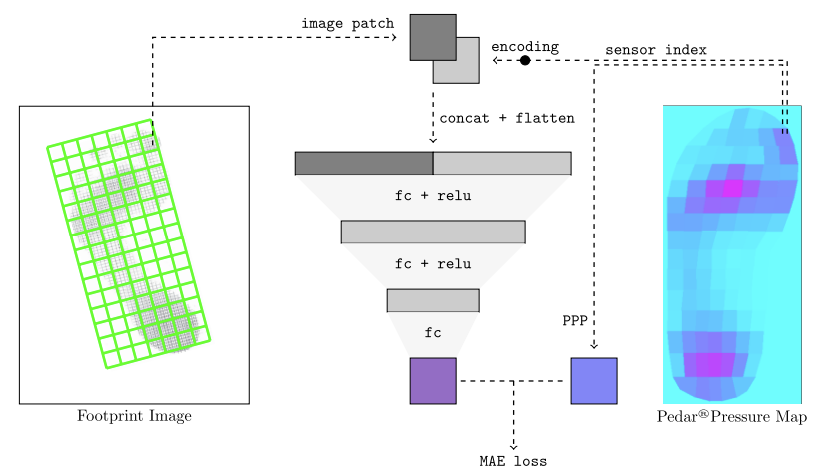
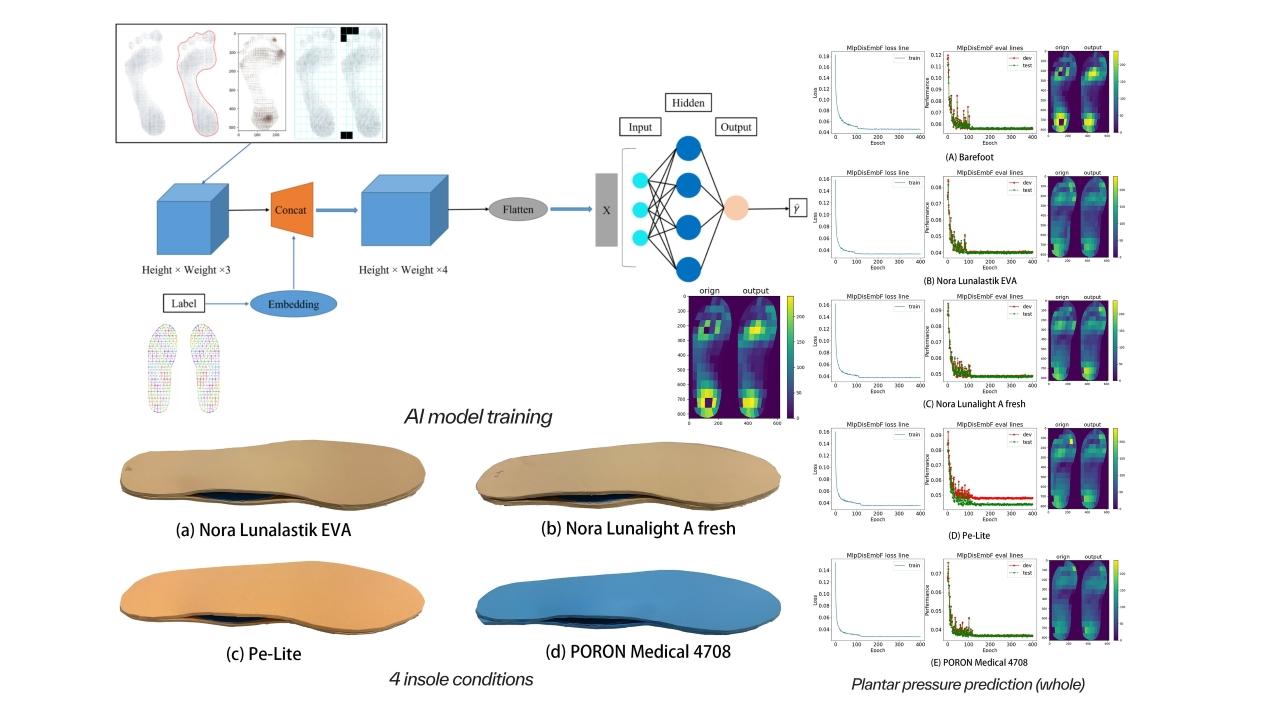
Assessing plantar pressure is vital for creating diabetic insoles and preventing diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs). Traditional methods require costly sensor-based equipment and expertise, making them time-consuming. This study suggests using ink footprint images to predict dynamic plantar pressure for barefoot and four insole types (Nora Lunalastik EVA, Nora Lunalight A Fresh, Pe-Lite, and PORON® Medical 4708) with a multilayer perceptron (MLP) neural network model. To provide tailored material recommendations, the foot is divided into five regions: toes, metatarsal heads, medial midfoot, lateral midfoot, and heel. A patch-based MLP with localization embedding links ink density to plantar pressure data. Ground-truth data from 52 diabetes patients is compiled into a dataset named diabetes-footprint-to-pressure for model training. The mean absolute error (MAE) for predicting plantar pressure across conditions ranges from 3.57% to 5.51%. This method streamlines plantar pressure assessment, allowing clinicians to recommend appropriate insole materials efficiently.