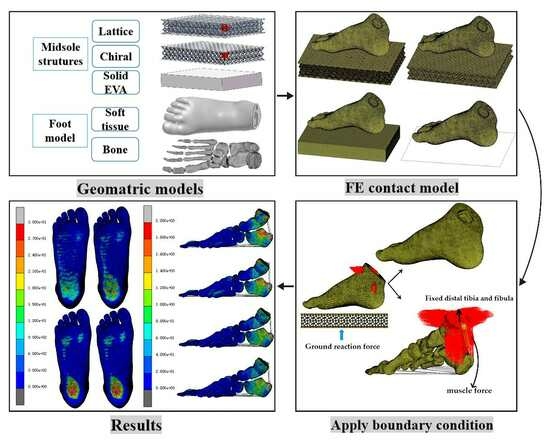
The foot, as the foundation of the human body, bears the vast majority of the body’s weight. Obese children bear more weight than healthy children in the process of walking and running. This study compared three footwear midsole structures (solid, lattice, and chiral) based on plantar pressure distribution and bone stress in obese and healthy children through numerical simulation. The preparation for the study included obtaining a thin-slice CT scan of a healthy 9-year-old boy’s right foot, and this study distinguished between a healthy and an obese child by applying external loadings of 25 kg and 50 kg in the finite element models. The simulation results showed that the plantar pressure was mainly concentrated in the forefoot and heel due to the distribution of gravity (first metatarsal, fourth metatarsal, and heel bone, corresponding to plantar regions M1, M4, and HM and HL) on the foot in normal standing. Compared with the lattice and solid EVA structures, in both healthy and obese children, the percentage reduction in plantar pressure due to the chiral structure in the areas M1, M4, HM, and HL was the largest with values of 38.69%, 34.25%, 64.24%, and 54.03% for an obese child and 33.99%, 28.25%, 56.08%, and 56.96% for a healthy child. On the other hand, higher pressures (15.19 kPa for an obese child and 5.42 kPa for a healthy child) were observed in the MF area when using the chiral structure than when using the other two structures, which means that this structure can transfer an amount of pressure from the heel to the arch, resulting in a release in the pressure at the heel region and providing support at the arch. In addition, the study found that the chiral structure was not highly sensitive to the external application of body weight. This indicates that the chiral structure is more stable than the other two structures and is minimally affected by changes in external conditions. The findings in this research lay the groundwork for clinical prevention and intervention in foot disorders in obese children and provide new research ideas for shoe midsole manufacturers
Zhou Q.
Niu W.
Gu B.