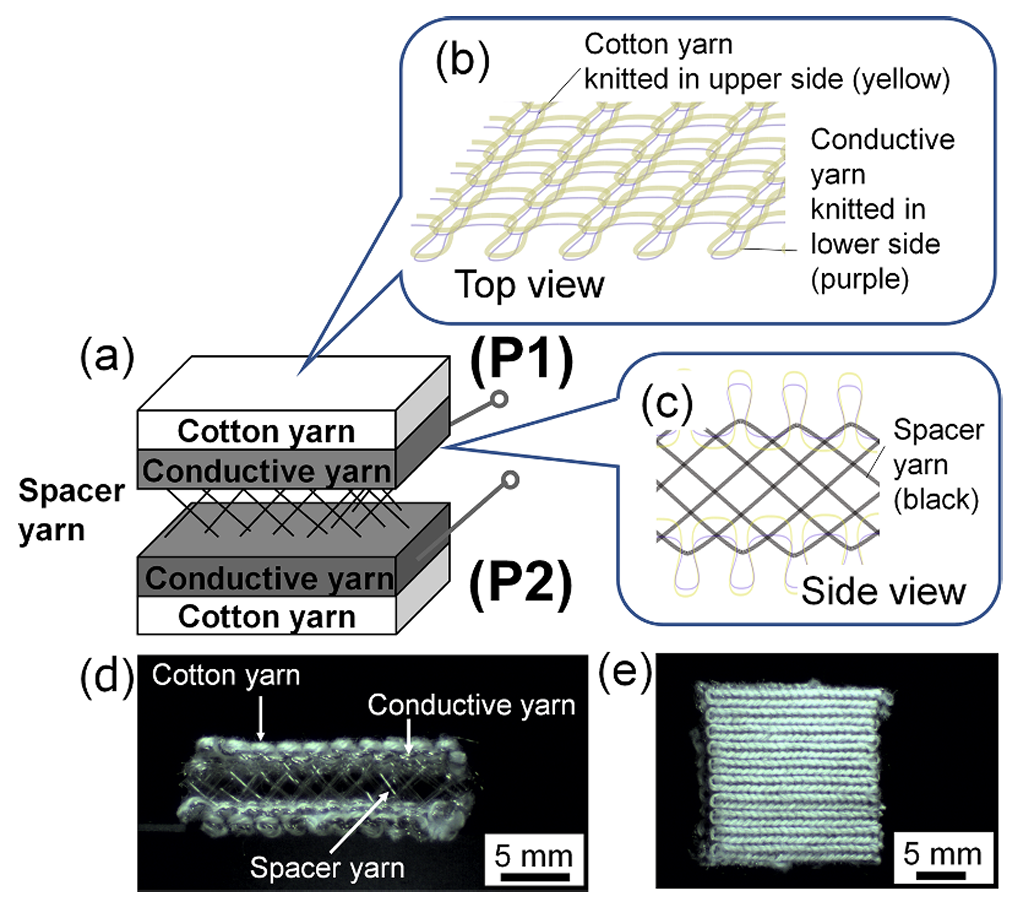
Attention toward automated driving has recently increased. This has also increased the need to monitor drivers’ actions, such as finger touch/pressure sensing on the steering wheel. This study demonstrates an active signal-generating spacer-fabric-type continuous touch/pressure sensor comprising five yarn layers: surface-insulating cotton, upper conductive, monofilament spacer, lower conductive and bottom-insulating cotton yarn. The sensor actively generates signals, and the magnitude of the voltage output through a diode bridge and capacitor circuit determines if the fingers are ‘not touching’, ‘touching’, ‘pushing’ or ‘pushing hard’. This demonstrates that the proposed sensor can be operated as an active signal-generating touch/pressure sensor and can also detect ‘pushing hard’ actions. Furthermore, the active signal-generating operation originates from the electromagnetic waves emitted by electrical appliances and cables powered by a commercial power supply frequency in the environment. The proposed sensor will contribute to developing high-cushioning touch/pressure sensors with low power consumption and excellent air permeability that can be used in electric and autonomous vehicles.
Tonomura K.
Ishii Y